Introduction
Oracle GoldenGate Microservices Architecture provides a REST API for managing service configurations. One common requirement is adjusting session timeout values to accommodate long-running operations or meet security policies. In this post, I’ll walk through how to safely update session timeout settings using the REST API without causing service disruptions.
The Challenge
By default, Oracle GoldenGate services have relatively short session timeouts:
sessionDurationSecs: 3600 seconds (1 hour)sessionInactiveSecs: 1800 seconds (30 minutes)
For operations requiring extended sessions, these defaults may be insufficient.
Balancing Convenience vs Security
When considering timeout modifications, it’s critical to carefully analyze the trade-off between operational convenience and security:
Longer timeouts provide:
- Reduced authentication overhead for long-running operations
- Better user experience for extended maintenance windows
- Fewer session interruptions during complex tasks
However, they also increase security risks:
- Extended exposure if credentials are compromised
- Longer window for unauthorized access if a session is hijacked
- Greater potential for unattended authenticated sessions
Best Practices:
- Set timeouts based on your specific operational requirements, not just convenience
- Consider your organization’s security policies and compliance requirements
- Use the minimum timeout duration that meets your operational needs
- Implement additional security controls (IP restrictions, MFA) when using longer timeouts
- Regularly audit and review timeout settings
- Document the business justification for non-default timeout values
For highly sensitive environments, shorter timeouts with more frequent re-authentication may be preferable despite the inconvenience.
The Solution
The key insight is to update only the configuration without forcing a service restart. The Oracle GoldenGate REST API allows configuration updates to be applied dynamically in many cases.
Understanding the API
According to the Oracle GoldenGate REST API documentation, the timeout settings are found in the authorizationDetails section:
- sessionDurationSecs: Duration of the authorization session (0 to 4,294,967,295 seconds)
- sessionInactiveSecs: Maximum inactivity time before session expires (0 to 4,294,967,295 seconds, 0 = unlimited)
- sessionReauthorizationLimit: Maximum number of times sessions can be reauthorized
Script 1: Modifying Timeout Values
Here’s the script that safely updates timeout values to 4 hours (14,400 seconds):
#!/bin/bash
# Configuration variables
dname='WEST'
timeout=14400 # 4 hours
hn='localhost'
netrc_file="$HOME/.ogg_netrc.sh"
sm_url="https://${hn}:9090/services/v2/deployments/ServiceManager/services/ServiceManager"
as_url="https://${hn}:9090/services/v2/deployments/${dname}/services/adminsrvr"
# Function to check if response is valid JSON
check_response() {
local response="$1"
local service_name="$2"
if echo "$response" | grep -q "<html>"; then
echo "Error: Received HTML error page for $service_name"
echo "$response"
return 1
fi
if [ -z "$response" ]; then
echo "Error: Empty response from $service_name"
return 1
fi
if ! echo "$response" | jq empty 2>/dev/null; then
echo "Error: Invalid JSON response from $service_name"
echo "Response was: $response"
return 1
fi
return 0
}
echo "=== Updating Admin Server Timeout Settings ==="
echo "NOTE: This will NOT restart the service automatically"
echo ""
# Get current config
as_response=$(curl --netrc-file "$netrc_file" -k -s \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Accept: application/json" \
-X GET "$as_url")
if ! check_response "$as_response" "Admin Server"; then
echo "Failed to get valid Admin Server config"
exit 1
fi
# Build new config - Only update the config section, DO NOT set status
echo "$as_response" | \
jq --arg timeout "$timeout" \
'.response.config.authorizationDetails.sessionInactiveSecs = ($timeout | tonumber) |
.response.config.authorizationDetails.sessionDurationSecs = ($timeout | tonumber) |
{config: .response.config}' > /tmp/admin_config.json
echo "Configuration to apply:"
cat /tmp/admin_config.json | jq
# Verify the config file is valid JSON
if ! jq empty /tmp/admin_config.json 2>/dev/null; then
echo "Generated invalid admin config JSON"
exit 1
fi
# Apply the update
echo ""
echo "Applying Admin Server timeout update (no restart)..."
as_patch_response=$(curl --netrc-file "$netrc_file" -k -s -L -X PATCH "$as_url" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Accept: application/json" \
-d @/tmp/admin_config.json)
echo "$as_patch_response" | jq
# Check if service is still responding
echo ""
echo "Verifying Admin Server is still responding..."
sleep 2
test_response=$(curl --netrc-file "$netrc_file" -k -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" "$as_url")
if [ "$test_response" = "200" ]; then
echo "✓ Admin Server is still up and responding"
else
echo "✗ WARNING: Admin Server returned status $test_response"
fi
echo ""
echo "=== Updating Service Manager Timeout Settings ==="
# Get current config
sm_response=$(curl --netrc-file "$netrc_file" -k -s \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Accept: application/json" \
-X GET "$sm_url")
if ! check_response "$sm_response" "Service Manager"; then
echo "Failed to get valid Service Manager config"
exit 1
fi
# Build new config
echo "$sm_response" | \
jq --arg timeout "$timeout" \
'.response.config.authorizationDetails.sessionInactiveSecs = ($timeout | tonumber) |
.response.config.authorizationDetails.sessionDurationSecs = ($timeout | tonumber) |
{config: .response.config}' > /tmp/sm_config.json
echo "Configuration to apply:"
cat /tmp/sm_config.json | jq
# Verify the config file is valid JSON
if ! jq empty /tmp/sm_config.json 2>/dev/null; then
echo "Generated invalid SM config JSON"
exit 1
fi
# Apply the update
echo ""
echo "Applying Service Manager timeout update (no restart)..."
sm_patch_response=$(curl --netrc-file "$netrc_file" -k -s -L -X PATCH "$sm_url" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Accept: application/json" \
-d @/tmp/sm_config.json)
echo "$sm_patch_response" | jq
# Check if service is still responding
echo ""
echo "Verifying Service Manager is still responding..."
sleep 2
test_response=$(curl --netrc-file "$netrc_file" -k -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" "$sm_url")
if [ "$test_response" = "200" ]; then
echo "✓ Service Manager is still up and responding"
else
echo "✗ WARNING: Service Manager returned status $test_response"
fi
echo ""
echo "=== Summary ==="
echo "Timeout settings updated successfully!"
echo "The changes may require a service restart to take full effect."
echo ""
echo "To restart services (if needed), use a separate restart script."
Script 2: Validating Current Configuration
To verify the changes or check current settings, use this validation script:
#!/bin/bash
# Configuration variables
dname='WEST'
hn='localhost'
netrc_file="$HOME/.ogg_netrc.sh"
sm_url="https://${hn}:9090/services/v2/deployments/ServiceManager/services/ServiceManager"
as_url="https://${hn}:9090/services/v2/deployments/${dname}/services/adminsrvr"
# Color codes for output
GREEN='\033[0;32m'
RED='\033[0;31m'
BLUE='\033[0;34m'
NC='\033[0m' # No Color
# Function to check if response is valid JSON
check_response() {
local response="$1"
local service_name="$2"
if echo "$response" | grep -q "<html>"; then
echo -e "${RED}Error: Received HTML error page for $service_name${NC}"
return 1
fi
if [ -z "$response" ]; then
echo -e "${RED}Error: Empty response from $service_name${NC}"
return 1
fi
if ! echo "$response" | jq empty 2>/dev/null; then
echo -e "${RED}Error: Invalid JSON response from $service_name${NC}"
return 1
fi
return 0
}
# Function to convert seconds to human readable format
format_time() {
local seconds=$1
if [ "$seconds" = "not set" ] || [ "$seconds" = "0" ]; then
echo "$seconds"
else
local hours=$((seconds / 3600))
local minutes=$(((seconds % 3600) / 60))
local secs=$((seconds % 60))
if [ $hours -gt 0 ]; then
echo "$seconds seconds (${hours}h ${minutes}m)"
elif [ $minutes -gt 0 ]; then
echo "$seconds seconds (${minutes}m ${secs}s)"
else
echo "$seconds seconds"
fi
fi
}
# Function to display timeout settings
display_service() {
local service_name="$1"
local service_url="$2"
local response
local session_inactive
local session_duration
local session_reauth_limit
echo "=== $service_name ==="
# Get current config
response=$(curl --netrc-file "$netrc_file" -k -s \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Accept: application/json" \
-X GET "$service_url")
if ! check_response "$response" "$service_name"; then
echo -e "${RED}✗ Failed to retrieve configuration${NC}\n"
return 1
fi
# Extract timeout values
session_inactive=$(echo "$response" | jq -r '.response.config.authorizationDetails.sessionInactiveSecs // "not set"')
session_duration=$(echo "$response" | jq -r '.response.config.authorizationDetails.sessionDurationSecs // "not set"')
session_reauth_limit=$(echo "$response" | jq -r '.response.config.authorizationDetails.sessionReauthorizationLimit // "not set"')
echo -e "${BLUE}Authorization Timeout Settings:${NC}"
echo " sessionInactiveSecs: $(format_time $session_inactive)"
echo " sessionDurationSecs: $(format_time $session_duration)"
echo " sessionReauthorizationLimit: $session_reauth_limit"
echo ""
return 0
}
# Main
echo "========================================"
echo "Current Timeout Configuration"
echo "========================================"
echo ""
# Check if netrc file exists
if [ ! -f "$netrc_file" ]; then
echo -e "${RED}Error: Netrc file not found: $netrc_file${NC}"
exit 1
fi
# Display Admin Server settings
display_service "Admin Server" "$as_url"
as_result=$?
# Display Service Manager settings
display_service "Service Manager" "$sm_url"
sm_result=$?
# Summary
echo "========================================"
if [ $as_result -eq 0 ] && [ $sm_result -eq 0 ]; then
echo -e "${GREEN}Configuration retrieved successfully${NC}"
exit 0
else
echo -e "${RED}Failed to retrieve some configurations${NC}"
exit 1
fi
How It Works
- No Status Field: We don’t include
"status": "restart"in the PATCH request - Config Only: I send only the
configobject with updated values - Health Check: After each update, I verify the service is still responding
- Error Handling: Comprehensive checks for HTML error pages and invalid JSON
The Update Process
- GET the current configuration
- Extract the existing config object
- Modify only the timeout values using jq
- PATCH back just the config section
- Verify the service is still responding
Example Output
Before Update:
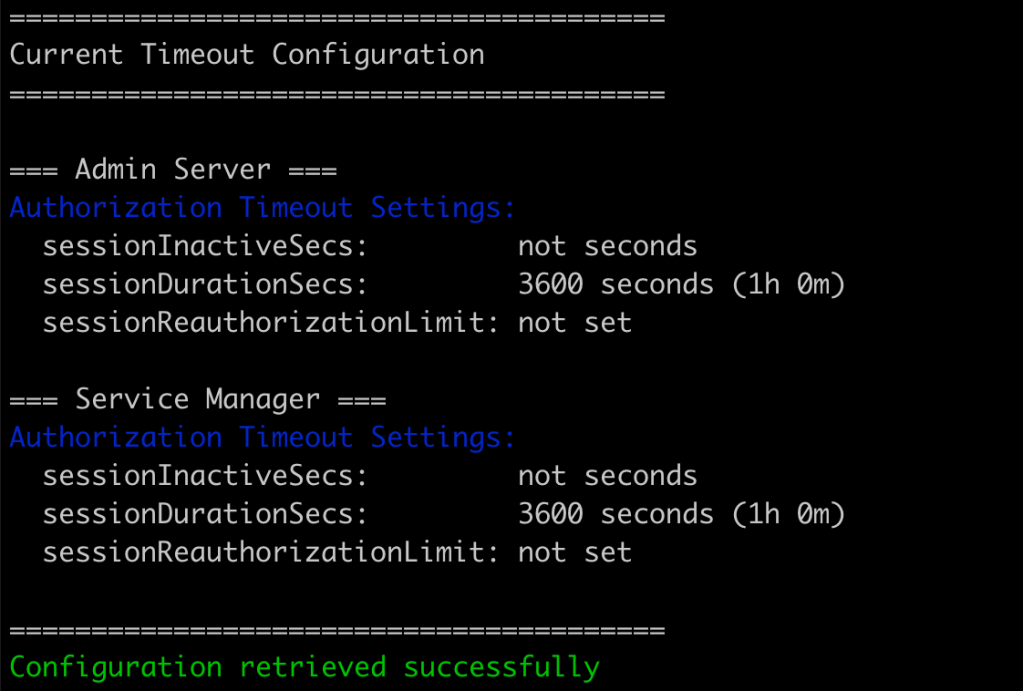
After Update:
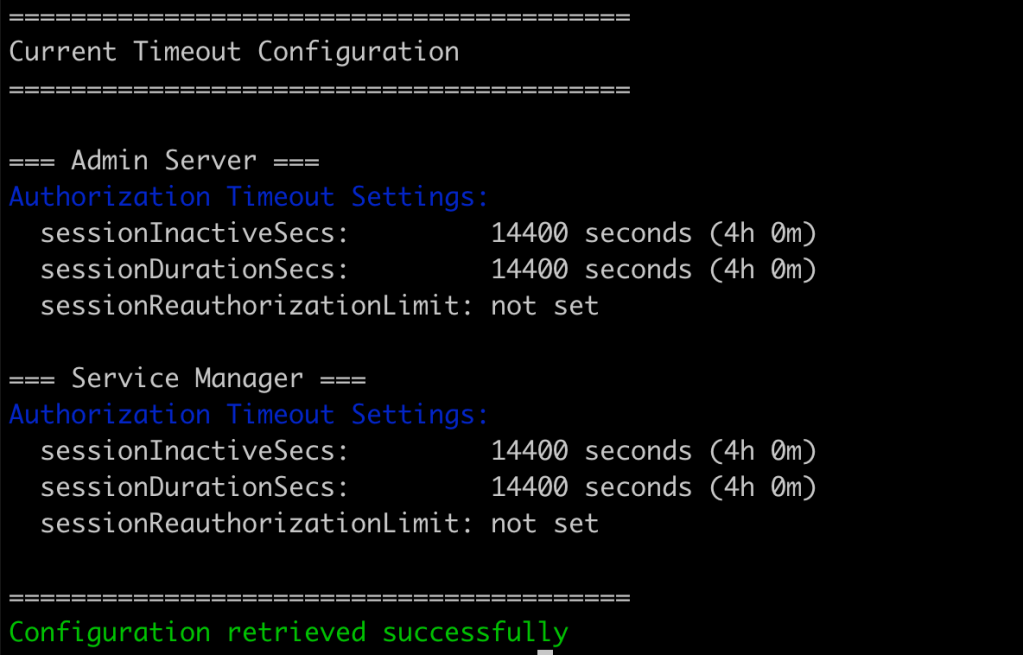
Important Notes
Authentication
These scripts use a netrc file for authentication:
netrc_file="$HOME/.ogg_netrc.sh"
Your netrc file should contain credentials in this format:
machine localhost
login <username>
password <password>
SSL/TLS
The scripts use -k flag with curl to skip certificate verification. In production, you should:
- Use proper SSL certificates
- Remove the
-kflag - Verify certificates properly
Timeout Values
The Oracle GoldenGate API accepts timeout values from 0 to 4,294,967,295 seconds:
- Setting to 0 means unlimited (use with caution)
- Maximum is approximately 136 years
- Common values: 3600 (1h), 14400 (4h), 28800 (8h)
When to Restart
While the configuration changes may apply dynamically, some environments might require a service restart for changes to take full effect. Monitor your sessions after the update to confirm the new timeouts are being enforced.
Conclusion
Updating session timeouts in Oracle GoldenGate Microservices is straightforward when you understand the correct API usage. The key is to update only the configuration without forcing a restart, which allows changes to be applied safely without service disruption.
These scripts provide a reliable, repeatable way to manage timeout settings across your GoldenGate environment. By separating the update and validation logic, you can safely modify settings and verify the results independently.
References
Have you encountered other challenges with Oracle GoldenGate REST API? Share your experiences in the comments below!

Leave a comment